 |
LehrFEM++ 1.0.0
A simple Finite Element Library for teaching
|
 |
LehrFEM++ 1.0.0
A simple Finite Element Library for teaching
|
#include <lf/geometry/point.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Point (Eigen::VectorXd coord) | |
| dim_t | DimLocal () const override |
| Dimension of the domain of this mapping. | |
| dim_t | DimGlobal () const override |
| Dimension of the image of this mapping. | |
| base::RefEl | RefEl () const override |
| The Reference element that defines the domain of this mapping. | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | Global (const Eigen::MatrixXd &local) const override |
| Map a number of points in local coordinates into the global coordinate system. | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | Jacobian (const Eigen::MatrixXd &local) const override |
Evaluate the jacobian of the mapping simultaneously at numPoints points. | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | JacobianInverseGramian (const Eigen::MatrixXd &local) const override |
Evaluate the Jacobian * Inverse Gramian ( \( J (J^T J)^{-1}\)) simultaneously at numPoints. | |
| Eigen::VectorXd | IntegrationElement (const Eigen::MatrixXd &local) const override |
| The integration element (factor appearing in integral transformation formula, see below) at number of evaluation points (specified in local coordinates). | |
| std::unique_ptr< Geometry > | SubGeometry (dim_t codim, dim_t i) const override |
Construct a new Geometry() object that describes the geometry of the i-th sub-entity with codimension=codim | |
| std::vector< std::unique_ptr< Geometry > > | ChildGeometry (const RefinementPattern &ref_pattern, base::dim_t codim) const override |
| the child geometry is just a copy of the point geometry | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry Public Member Functions inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry | |
| virtual bool | isAffine () const |
| element shape by affine mapping from reference element | |
| virtual | ~Geometry ()=default |
| Virtual destructor. | |
Private Attributes | |
| Eigen::VectorXd | coord_ |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry Public Types inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry | |
| using | dim_t = base::RefEl::dim_t |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry Protected Member Functions inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry | |
| Geometry ()=default | |
| Geometry (const Geometry &)=default | |
| Geometry (Geometry &&)=default | |
| Geometry & | operator= (const Geometry &)=default |
| Geometry & | operator= (Geometry &&)=default |
 Related Symbols inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry Related Symbols inherited from lf::geometry::Geometry | |
| void | PrintInfo (std::ostream &o, const Geometry &geom, int output_ctrl=0) |
| Diagnostic output operator for Geometry. | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &stream, const Geometry &geom) |
Operator overload to print a Geometry to a stream, such as std::cout | |
|
inlineexplicit |
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
the child geometry is just a copy of the point geometry
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 30 of file point.cc.
References coord_, lf::base::RefEl::kPoint(), lf::geometry::RefinementPattern::NumChildren(), lf::geometry::RefinementPattern::RefEl(), and lf::base::RefEl::ToString().
|
inlinenodiscardoverridevirtual |
Dimension of the image of this mapping.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 16 of file point.h.
References coord_.
Referenced by Jacobian().
|
inlinenodiscardoverridevirtual |
Dimension of the domain of this mapping.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Map a number of points in local coordinates into the global coordinate system.
| local | A Matrix of size DimLocal() x numPoints that contains in its columns the coordinates of the points at which the mapping function should be evaluated. |
DimGlobal() x numPoints that contains the mapped points as column vectors. Here numPoints is the number of columns of the matrix passed in the local argument. \[ \mathtt{Global}\left(\left[\widehat{x}^1,\ldots,\widehat{x}^k\right]\right) = \left[ \mathbf{\Phi}_K(\widehat{x}^1),\ldots,\mathbf{\Phi}_K(\widehat{x}^k)\right]\;,\quad \widehat{x}^{\ell}\in\widehat{K}\;, \]
where \(\mathbf{\Phi}\) is the mapping taking the reference element to the current element \(K\).This method provides a complete description of the shape of an entity through a parameterization over the corresponding reference element = parameter domain. The method takes as arguments a number of coordinate vectors of points in the reference element. For the sake of efficiency, these coordinate vectors are passed as the columns of a dynamic matrix type as supplied by Eigen.
For instance, this method is used in lf::geometry::Corners()
Additional explanations in Lecture Document Paragraph 2.7.5.17.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 4 of file point.cc.
References coord_.
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
The integration element (factor appearing in integral transformation formula, see below) at number of evaluation points (specified in local coordinates).
| local | A Matrix of size DimLocal() x numPoints that contains the evaluation points (in local = reference coordinates) as column vectors. |
numPoints x 1 that contains the integration elements at every evaluation point.For a transformation \( \Phi : K \mapsto R^{\text{DimGlobal}}\) with Jacobian \( D\Phi : K \mapsto R^{\text{DimGlobal} \times \text{DimLocal}} \) the integration element \( g \) at point \( \xi \in K \) is defined by
\[ g(\xi) := \sqrt{\mathrm{det}\left|D\Phi^T(\xi) D\Phi(\xi) \right|} \]
More information also related to the use of local quadrature rules is given in Lecture Document Paragraph 2.7.5.24.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Evaluate the jacobian of the mapping simultaneously at numPoints points.
| local | A Matrix of size DimLocal x numPoints that contains the evaluation points as column vectors |
DimGlobal() x (DimLocal() * numPoints) that contains the jacobians at the evaluation points.This method allows access to the derivative of the parametrization mapping in a number of points, passed as the columns of a dynamic matrix. The derivative of the parametrization in a point is a Jacobian matrix of size ‘DimGlobal() x DimLocal()’. For the sake of efficiency, these matrices are stacked horizontally and returned as one big dynamic matrix. Use Eigen's ‘block()’ method of Eigen::MatrixXd to extract the individual Jacobians from the returned matrix.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 10 of file point.cc.
References DimGlobal().
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Evaluate the Jacobian * Inverse Gramian ( \( J (J^T J)^{-1}\)) simultaneously at numPoints.
| local | A Matrix of size DimLocal() x numPoints that contains the evaluation points as column vectors. |
DimGlobal() x (DimLocal() * numPoints) that contains the Jacobian multiplied with the Inverse Gramian ( \( J (J^T J)^{-1}\)) at every evaluation point.DimLocal() == DimGlobal() then \( J (J^T J)^{-1} = J^{-T} \), i.e. this method returns the inverse of the transposed jacobian.If both dimensions agree and have the value D, then the method returns the transposed of the inverse Jacobians of the transformation at the passed points. These are square DxD matrices.
To retrieve the j-th inverse transposed Jacobian from the returned matrix, use the block methdod of Eigen (case (D = DimLocal()) == DimGlobal())
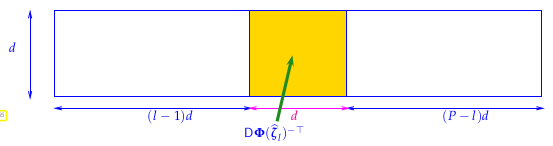
More explanations in Paragraph 2.8.3.14.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
|
inlinenodiscardoverridevirtual |
The Reference element that defines the domain of this mapping.
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 18 of file point.h.
References lf::base::RefEl::kPoint().
|
nodiscardoverridevirtual |
Construct a new Geometry() object that describes the geometry of the i-th sub-entity with codimension=codim
| codim | The codimension of the sub-entity (w.r.t. DimLocal()) |
| i | The zero-based index of the sub-entity. |
Let \( \mathbf{\Phi} : K \mapsto \mathbb{R}^\text{DimGlobal} \) be the mapping of this Geometry object and let \( \mathbf{\xi} :
\mathbb{R}^{\text{DimLocal}-codim} \mapsto K\) be the first-order mapping that maps the reference element RefEl().SubType(codim,i) to the i-th sub-entity of RefEl(). I.e. for every node \( \mathbf{n_j} \) of RefEl().SubType(codim,i) it holds that \( \mathbf{\xi}(\mathbf{n_j}) =
\) RefEl().NodeCoords(RefEl().SubSubEntity2SubEntity(codim, i, DimLocal()-codim, j)).
Then the geometry element returned by this method describes exactly the mapping \( \mathbf{\Phi} \circ \mathbf{\xi} \)
Implements lf::geometry::Geometry.
Definition at line 23 of file point.cc.
References coord_.
|
private |
Definition at line 41 of file point.h.
Referenced by ChildGeometry(), DimGlobal(), Global(), Point(), and SubGeometry().